Reionization is one of the most exciting epochs of our universe, where the first generation stars and galaxies formed and begun a global impact by ionizing the neutral hydrogen in that epoch. High-z galaxies, especially to the first galaxies in the epoch of reionization, would help us to reveal the structure formation of our Universe through the cosmic time. At Peking University and Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, we study reionization and high-z galaxies by searching and identifying the narrowband imaging selected Lyman alpha emitting galaxies (LAEs) via the M2FS project and the LAGER project (Lyman Alpha Galaxies in the Epoch of Reionization). Based on these collaborations, we are preparing for the upcoming and the next-generation LAE studies led by CSST, which will be the first Chinese space optical telescope.
M2FS:
The Magellan M2FS survey is a spectroscopic survey of high-redshift, luminous galaxies over three square degrees on the sky, aiming to build a large and homogeneous sample of Lyα emitters (LAEs) at redshift z ~ 5.7 and 6.5, and Lyman-break galaxies (LBGs) at 5.5 < z < 6.7. The survey covers five well studied fields, including the Subaru XMM/Newton Deep Survey, Extended Chandra Deep Field South, COSMOS, A370, and SSA22. These fields have very deep optical imaging data in a series of broad and narrow bands, allowing for the efficient selection of galaxy candidates. Spectroscopic observations are carried out using the multi-object spectrograph M2FS on the 6.5 m Magellan Clay telescope. When the program is completed, we expect to identify more than 300 bright LAEs at z ~ 5.7 and 6.5, and a substantial number of LBGs at z ~ 6. This unique sample will be used to study a variety of galaxy properties and to search for large protoclusters. Furthermore, the statistical properties of these galaxies will be used to probe cosmic reionization. See Jiang et al. (2017) for the program overview.
We have obtained a few exciting results. We have discovered a sample of extremely luminous LAEs. Some of them are brighter than `CR7', a galaxy thought to be powered by Pop III stars or a direct core collapse black hole. We have detected diffuse Lyα halos around star-forming galaxies at z ≈ 5.7 by stacking 310 LAEs. This is the first time that this topic is studied using a large and spectroscopically confirmed sample. We have discovered a giant protocluster that has a volume of ~ 353 cMpc3. Its overdensity is very high ~5.6, and its present-day mass is ~ 3.6 × 1015 M⨀. This makes it the most massive protocluster at high redshift. Such objects may be ideal probes for understanding early structure formation.
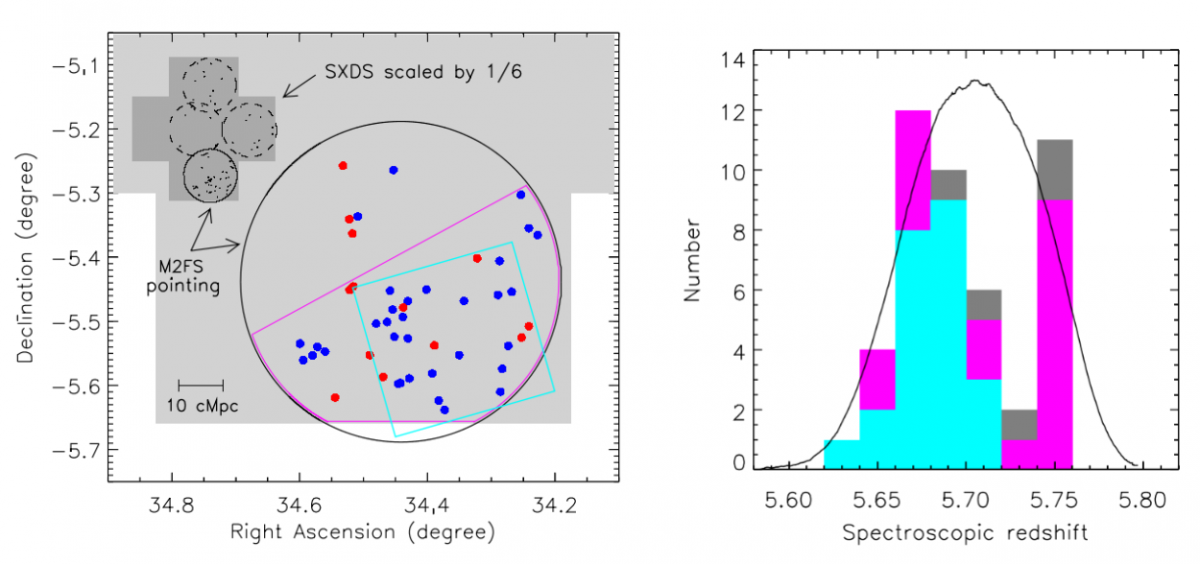
Figure 1. Discovery of a giant protocluster at z~5.7.
LAGER:
LAGER is a narrowband survey project to identify galaxies at z~7. The survey is conducted as an international collaboration between astronomers in China (including SHAO and PKU), US, and Chile using the Dark Energy Cam at the CTIO Blanco telescope. With a specially built narrowband filter NB964, we search and identify galaxies at z=6.94+/-0.04 with strong Lyman-alpha emission lines, and use this LAE sample to probe the epoch of reionization. We also study the neutral hydrogen in that epoch collaborated with Australian astronomers.
We have had the record of the largest LAE sample at z~7 with LAGER. In the first LAGER field, LAGERE-COSMOS, we have discovered 23 LAE candidates at z~7, which was the largest LAE sample at that redshift then (Zheng et al. 2017, see Figure 2). These LAEs show an excess of numbers at the luminous end, which supports the hypothesis of ionized bubbles contributed by clustering of galaxies in that epoch. To date, LAGER still holds the record of the largest LAE sample at z~7, which is 150+ LAEs at z~7 selected from 4 LAGER fields. With this sample, we can apply several tests, such as Lyman-alpha luminosity function test, Lyman-alpha equivalent-width test, galaxy clustering test, void statistics test, etc., to probe the epoch of reionization statistically.

Figure 2. False color image of a 2 square degree region of the LAGER survey field in COSMOS, created from images taken in the optical at 500 nm (blue), in the near-infrared at 920 nm (red), and in a narrow-band filter centered at 964 nm (green). The last is sensitive to hydrogen Lyman alpha emission at z ~ 7. The small white boxes indicate the positions of the 23 LAEs discovered in the survey (Zheng et al. 2017). The detailed insets (yellow) show two of the brightest LAEs; they are 0.5 arcminutes on a side, and the white circles are 5 arcseconds in diameter. Image Credit: Zhen-Ya Zheng (SHAO) & Junxian Wang (USTC).
References:
- "A Magellan M2FS Spectroscopic Survey of Galaxies at 5.5 < z < 6.8: Program Overview and a Sample of the Brightest Lyα Emitters", Jiang, L., Shen, Y., Bian, F., Zheng, Z.-Y., Wu, J., Oyarzún, G. A., Blanc, G. A., Fan, X., Ho, L. C., Infante, L., Wang, R., Wu, X.-B., Mateo, M., Bailey, J. I., Crane, J. D., Olszewski, E. W., Shectman, S., Thompson, I., Walker, M. G., 2017, The Astrophysical Journal
- "A giant protocluster of galaxies at redshift 5.7", Jiang, L., Wu, J., Bian, F., Chiang, Y.-K., Ho, L. C., Shen, Y., Zheng, Z.-Y., Bailey, J. I., Blanc, G. A., Crane, J. D., Fan, X., Mateo, M., Olszewski, E. W., Oyarzún, G. A., Wang, R., Wu, X.-B., 2018, Nature Astronomy
- "First Results from the Lyman Alpha Galaxies in the Epoch of Reionization (LAGER) Survey: Cosmological Reionization at z ̃ 7", Zheng, Z.-Y., Wang, J., Rhoads, J., Infante, L., Malhotra, S., Hu, W., Walker, A. R., Jiang, L., Jiang, C., Hibon, P., Gonzalez, A., Kong, X., Zheng, X., Galaz, G., Barrientos, L. F., 2017, The Astrophysical Journal
- "Design for the First Narrowband Filter for the Dark Energy Camera: Optimizing the LAGER Survey for z ̃ 7 Galaxies", Zheng, Z.-Y., Rhoads, J. E., Wang, J.-X., Malhotra, S., Walker, A., Mooney, T., Jiang, C., Hu, W., Hibon, P., Jiang, L., Infante, L., Barrientos, L. F., Galaz, G., Valdes, F., Wester, W., Yang, H., Coughlin, A., Harish, S., Kang, W., Khostovan, A. A., Kong, X., Perez, L. A., Pharo, J., Wold, I., Zheng, X., 2019, Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific